- Home
- About Us
- Product
- Adapters & Reducers
- Brake Nuts
- CNC Machined Parts
- Copper Jumpers
- Double Compression Cable Glands
- Fabrication Works
- Flanges
- FRP Canopies
- Hydraulic Fittings
- Injection Molding Products
- Junction Boxes
- Nozzles
- Rebar Coupler
- S S Inserts
- Shafts
- Single Clamp, Dual Clamp And Quadra Foil
- Stainless Steel Bellow
- Stopper Plugs
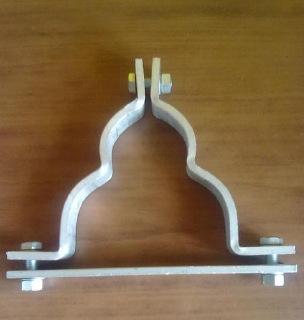
- Trefoil Clamps
- Gallery
- contact